Laser dentistry is a subspecialty of dentistry that treats different dental issues with concentrated light beams. "Laser" is an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Radiation Emission, which in dentistry, allows for accurate tissue removal or cutting, reducing invasiveness and improving patient comfort during procedures. The technique accelerates healing times, decreases pain, and improves accuracy in numerous dental operations, revolutionizing the field.
Hard tissue lasers and soft tissue lasers are the two main types of lasers utilised in dentistry. Hard tissues, like bone and teeth, are sliced through with hard tissue lasers, commonly used for cavity diagnosis and removal, filling preparation for teeth, and bone formation during medical operations. Gums and other soft tissues are sliced and shaped with soft tissue lasers. They are perfect for treating gum disease by eliminating contaminated tissue, straightening the gums, and eliminating soft tissue folds. Cosmetic and health-maintenance dentistry operations are examples of other sorts of laser dentistry procedures. A laser is used for various purposes, including scar tissue reduction, whitening procedure acceleration, filling contouring, and small-scale dental enamel removal.
Other applications of lasers in dentistry are to remove damaged tissue and identify early indicators of tooth disease. Lasers are used to eliminate mouth lesions or a tiny sample of tissue for a biopsy. They aid in the cleansing and disinfection of root canals with extreme precision. Brace implantation is facilitated and partially erupted teeth are exposed with the help of lasers.
The advantages of laser dentistry include precision and accuracy, reduced pain and discomfort, faster healing, and minimized bleeding. Tissue is sliced and removed with extraordinary precision with the help of lasers, keeping more of the structural integrity intact with the help of lasers. Anaesthesia is not always necessary since laser treatments are less painful than traditional ones. Lasers cause less bleeding and edema, and faster recovery time since tissue damage is minimal during laser operations. The high-energy beam lowers the chance of bacterial infections by sterilizing the area. Blood clotting is encouraged by lasers, which help to reduce bleeding both during and after treatments.
Tissue damage, eye damage, infection risk, and technical sensitivity are among the dangers associated with dental laser treatment. The surrounding tissues sustain damage or burns when lasers are used incorrectly. The laser beam causes serious eye injuries when appropriate measures are not followed, requiring suitable eye protection. The risk of infection remains, though diminished if the equipment is not sufficiently sanitized. The dentist's expertise and the kind of laser they employ have a major impact on how well a laser treatment works.
A single dental laser machine costs anywhere from $500 to over $100,000 in the US, while laser treatments ranges from $75 to $2000 in the US. The location, level of skill of the dentist, kind of procedure, and complexity of the treatment affect how much it costs. Laser treatments are more costly than traditional approaches since laser equipment is expensive and requires specific training for dentists. Insurance coverage for laser dentistry differs and sometimes does not cover the entire cost, particularly for cosmetic operations.
What is Laser Dentistry?
Laser dentistry is a form of dental treatment that employs direct light amplification. Laser dentistry is the use of laser or Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation technology to execute different dental processes. Lasers' concentrated light energy allows them to precisely cut and shape soft and hard tissues. The purpose of laser dentistry is to offer dental operations a more accurate, minimally intrusive treatment alternative. Various therapies are more effective and comfortable when tissue is sliced, contoured, and removed using lasers. They support gum surgery, tooth whitening, cavity preparation, and other procedures.
Bone and teeth are sliced with hard tissue lasers which function at wavelengths that water and the mineral hydroxyapatite absorb, such as Erbium YAG and Erbium chromium lasers. The lasers work well for cavity detection and removal, reshaping bone during surgical treatments, and preparing teeth for fillings. Soft tissue lasers are excellent for slicing and solidifying soft tissues since they target the hemoglobin, a protein found in blood, and water. CO2 and diode dental laser are two variations utilised to treat periodontal disease by eliminating infected tissue, molding and contouring the gums, and scraping lesions and creases in soft tissue.
Hard tissue laser and soft tissue laser differ in wavelength, applications, and absorption. Hard tissue lasers use wavelengths specifically targeted at hard structures while soft tissue lasers use wavelengths accepted by soft tissues. Soft tissue lasers are utilised for gums and other soft tissues, while hard tissue lasers are utilised for methods involving teeth and bones. Soft tissue lasers are intended for blood and water components, whereas hard tissue lasers are accepted by teeth and bone minerals. Dental laser treatment employs specific lasers for hard and soft tissues, which improves dental treatment through increased precision, decreased discomfort, and faster recovery.
What is the History of Laser Dentistry?
The history of Laser dentistry dates back to its exploration in the 1960s after the invention of LASER. Theodore Maiman invented the first working laser in 1960 using a ruby crystal. The "father of laser medicine," Dr. Leon Goldman, presented the first studies on the impact of lasers on tooth tissues in 1964. Goldman's research paved the way for potential uses of lasers in dentistry by demonstrating their ability to alter both soft and hard tissues in the mouth.
The 1980s saw the introduction of lasers into dentistry procedures. The Nd:YAG laser was given FDA approval in 1989 to be used in dentistry for soft tissue operations, which signaled the start of the actual use of laser technology in dental procedures.
Several changes occurred since lasers' first application in dentistry in the 1980s. The current focus of laser technology is on increasing various treatable ailments, expediting operation times, and enhancing the patient experience. The future of high-tech, minimally invasive dental care is represented by the combination of laser equipment with digital dentistry technologies such as CAD/CAM.
What are the Types of Lasers used in Dentistry?
The types of lasers used in dentistry are listed below.
- Carbon dioxide lasers: CO2 lasers produce a high-energy beam strongly absorbed by water and precisely vaporize soft tissues at a wavelength of 10,600 nm. The lasers make clean cuts with little bleeding, which makes them useful for soft tissue procedures including gum contouring, biopsies, and lesion excision. CO2 lasers encourage quicker recovery and less pain following surgery.
- Diode lasers: Diode lasers are perfect for soft tissue operations since they absorb predominantly melanin and hemoglobin at wavelengths between 800 and 980 nm. They are employed in periodontal procedures such as laser teeth whitening, scaling and root planing, and gingivectomy. Diode lasers are well known for their effectiveness in lowering microorganisms and encouraging tissue regeneration. They are portable and reasonably priced.
- Erbium lasers: Erbium lasers, such as Er-YAG and Er, Cr-YSGG, are appropriate for soft and hard tissues since hydroxyapatite and water both absorb light at wavelengths of 2,940 and 2,780 nm, respectively. The lasers provide the least amount of thermal damage when utilised for soft tissue operations, bone contouring, and cavity preparation. Their versatility and capacity to deliver accurate, minimally intrusive treatments make them highly prized in contemporary dentistry.
- Argon lasers: Argon lasers are excellent for soft tissue treatments and curing composite resins because they operate at wavelengths of 488 nm and 514 nm, and are largely absorbed by pigments and hemoglobin. They are utilised in restorative dentistry to improve the polymerization of light-cured materials to ensure stronger and longer-lasting dental restorations. Argon lasers are used to manage bleeding during operations and for minor oral surgery.
- Nd-YAG lasers: Nd-YAG lasers are useful for cutting and coagulating because their 1,064 nm wavelength is significantly absorbed by pigments in soft tissues. They are used in endodontic treatments to sterilize root canals and in periodontal therapy to eliminate germs and diseased tissue. Nd-YAG lasers are renowned for their capacity to penetrate deeply, support hemostasis, and expedite tissue repair.
How does Laser Dentistry Work?
Laser dentistry works by utilizing focused light energy in the form of a laser beam to carry out precise dental procedures. The laser light's interaction with the tissue varies based on the kind of laser being utilised and the particular operation being carried out. Ablation, vaporisation, coagulation, and stimulation of tissue repair are the main ways that lasers work in dentistry.
Lasers employ powerful, concentrated light to either evaporate or eliminate tissue. Lasers, like the Erbium laser, break down hard tissues such as teeth and bone for cavity preparation or bone contouring by emitting wavelengths that water and hydroxyapatite absorb.
Diode and CO2 lasers for soft tissues emit wavelengths absorbed by hemoglobin and water, enabling accurate cutting, shaping, or removal of gum tissue. Blood vessels are made to coagulate using lasers, stopping bleeding during surgeries. The high-energy beam minimizes bleeding and suture requirements by sealing blood arteries as it cuts. Certain lasers stimulate tissue repair, accelerating healing and reducing inflammation in soft tissue procedures. For example, lower energy levels are used in low-level laser treatment (LLLT) to improve cell regeneration and lessen pain and edema. Anesthetic requirements and surgical complications are reduced since laser treatments are minimally intrusive. Sterilizing properties of lasers in treatment regions decreases the risk of infection.
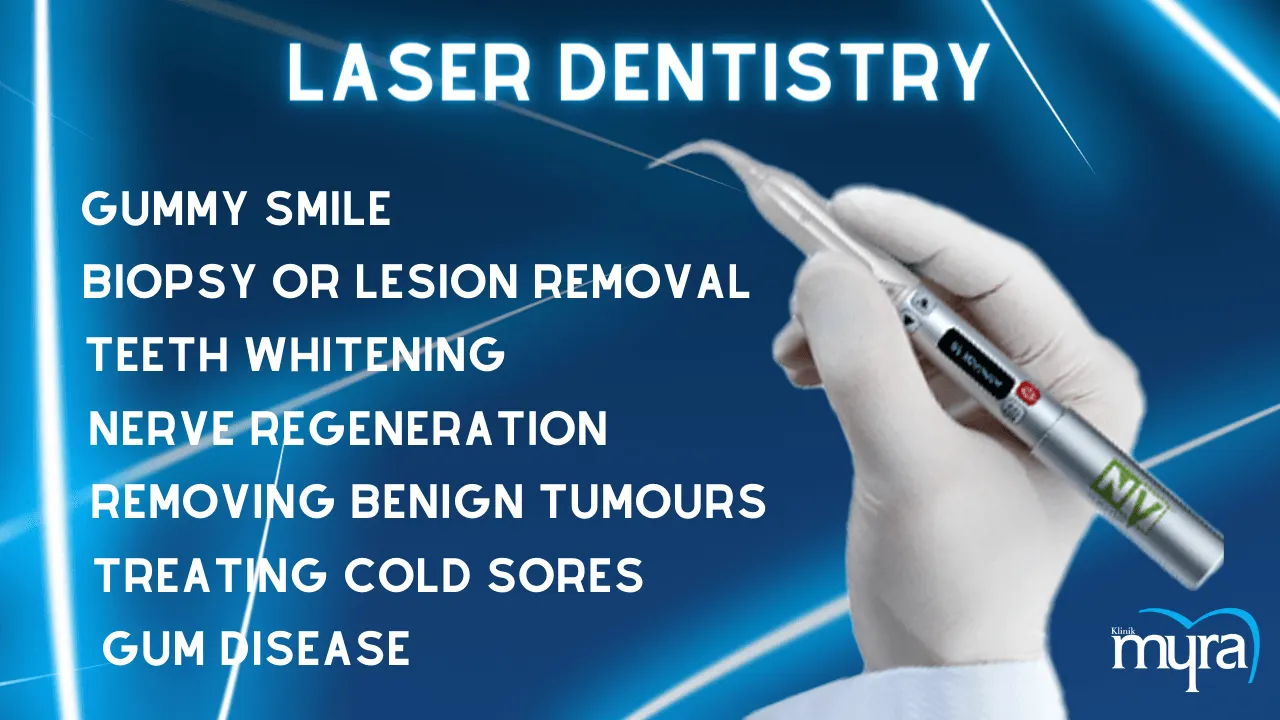
What are the Applications of Laser Dentistry?
The applications of laser dentistry are listed below,
- Tooth Decay: Laser dentistry removes decaying areas of a tooth to prepare the surrounding enamel for a filling, without conventional drilling. Laser dentistry for cavities lessens the need for anesthetic and is less uncomfortable. "Applications" in laser dentistry relate to the different clinical ways laser technology is used to carry out dental operations, including periodontal therapy, soft tissue surgery, and cavity preparation. Comparing the applications to conventional procedures yields advantages such as decreased pain, fewer bleeds, and quicker mending durations.
- Gum Disease: Lasers eliminate germs and sick tissue from the gums to encourage regeneration and healing. Bleeding, edema, and discomfort are reduced using the technique instead of traditional procedures.
- Biopsy or Lesion Removal: Biopsy is a dental laser treatment that eliminates lesions from the mouth and cuts a small amount of tissue for evaluation. The method reduces bleeding and expedites the healing process.
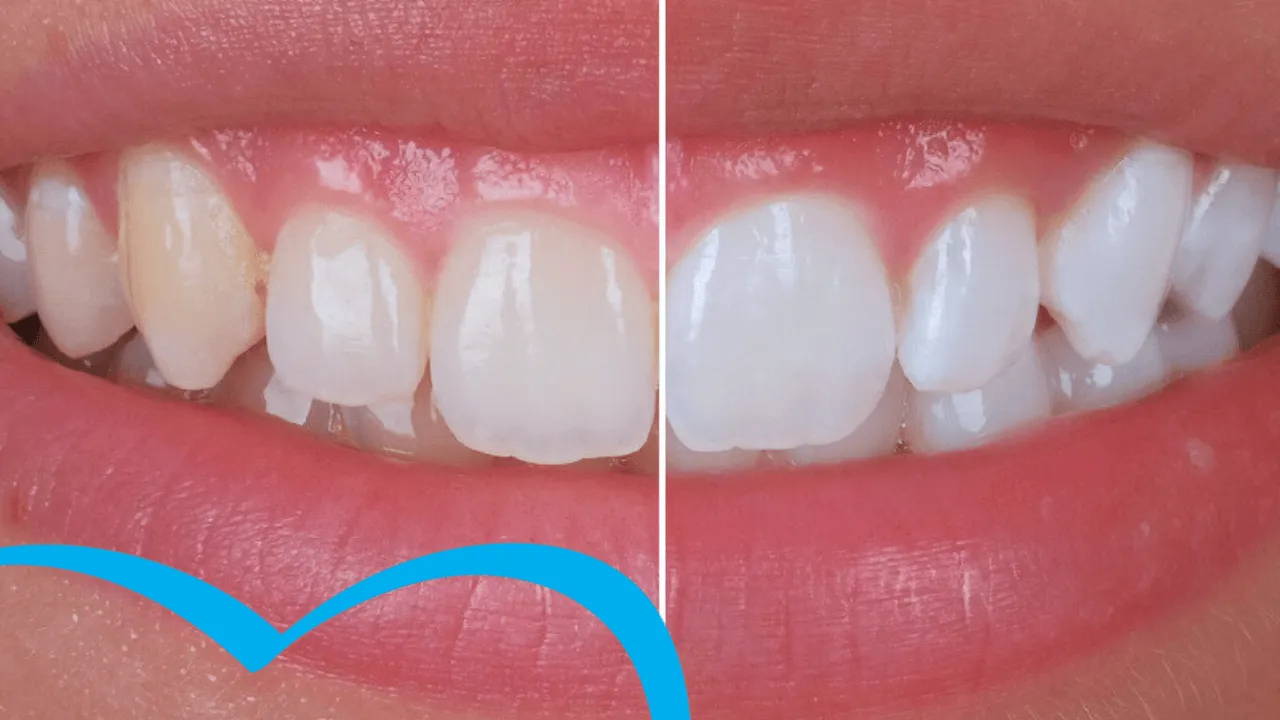
- Teeth Whitening: A bleaching substance is applied to the teeth and is activated using laser radiation to whiten teeth. The procedure produces more rapid and obvious results while accelerating the whitening effect.
- Gummy Smile: Lasers are used to restructure excessive gum tissue, exposing more of the teeth and enhancing the smile's appearance. The method causes less discomfort and expedites the healing process.
- Removing Benign tumours: Benign tumours are successfully removed from different mouth areas using lasers without incisions, expediting the healing process and lowering the chance of infection.
- Nerve Regeneration: Lasers help injured dental nerves regenerate by promoting nerve development and restoration according to recent research. Research on the application is continuous and is used in other treatments.
- Treating Cold Sores: Cold sore pain and healing time are decreased with laser treatments. Lasers reduce the frequency and intensity of subsequent outbreaks by focusing on the virus at its source.
1. Tooth Decay
Tooth decay or dental caries or cavities, is a disorder in which the acid produced by oral bacteria damages the tooth's hard surface, mainly the enamel. The bacteria generate acid, which demineralizes and degrades the tooth structure, as a consequence of feeding on the sugars and starches that remain on teeth. Tooth decay causes discomfort, illness, and tooth loss if left untreated. It penetrates through the enamel to the dentin and even the pulp.
Decaying tooth tissue is targeted and removed using a concentrated light beam in laser dentistry. A dental laser treatment accurately vaporizes the decaying area, allowing for a more cautious approach when opposed to conventional drilling procedures. The method gets teeth ready for a filling by removing microorganisms from the cavity's surface or conducting a laser teeth cleaning. Patients experience less discomfort when tooth decay is treated using lasers, which minimizes the need for local anesthetic. Lasers aid in sterilizing the cavity region, reducing the risk of a secondary bacterial infection.
Tooth decay is effectively treated using laser dentistry, especially for minor to moderate cavities. More healthy tooth structures are preserved due to the laser's accuracy, good for the tooth's overall integrity. Patients have a better dental experience since they endure less pain and discomfort during and after the operation. The laser's capacity to sterilize the area lengthens the fillings' lifespan by lowering the risk of recurring deterioration. Not all cavities benefit from laser treatment, particularly when they are deep or difficult to access. Traditional drilling techniques are still required in certain situations. Laser dentistry provides a useful substitute for traditional techniques when used correctly for Teeth Decays, enhancing patient comfort and treatment results.
2. Gum Disease
Periodontal disease or gum disease, is an inflammatory illness that affects the tissues that support and surround the teeth. Gingivitis is the first stage, characterized by red, swollen, and sometimes bleeding gums. Gingivitis develops into a more severe type called periodontitis when untreated in which the gums separate from the teeth and create contaminated pockets. It causes the bone and connective tissue that hold teeth in place to break down, leading to tooth loss.
A dental laser treatment resolves gum disease by eradicating germs from the periodontal pockets and inflamed gum tissue. Better healing is facilitated by the laser's energy, which targets bacteria and sick tissue while preserving healthy tissue. The laser lowers the bacterial load and aids in the removal of illness while sterilizing the region during the treatment. Lasers promote the regeneration of healthy tissue and the gums' reattachment to the teeth. The procedure lessens the patient's bleeding, swelling, and discomfort and is less invasive than more conventional techniques like scaling and root planing combined with surgery.
Gum disease is effectively treated using laser dentistry, especially when it comes to minimizing pocket depth and encouraging the growth of new, healthy tissue. Laser dental surgery reduces inflammation and bacterial counts, improving periodontal health according to studies. Patients experience less pain and recover more quickly compared to traditional surgical approaches. Healthier gum and bone structures are preserved due to the laser's precision, which enables targeted treatment. The degree of gum disease and the patient's commitment to maintaining proper dental hygiene after treatment impacts how well laser therapy works. The best outcomes are obtained when combined with other therapies although lasers are a useful tool for treating periodontal disease.
3. Biopsy or Lesion Removal
A biopsy or lesion removal is a process of taking a little sample of tissue out of the body to examine under a microscope to identify a condition, such as cancer. Removing aberrant tissues, such as benign tumours, cysts, or other growths in the mouth is called lesion removal. The procedures are necessary to ensure that any aberrant tissue is free from health risks and to diagnose and treat various oral disorders.
A concentrated beam of light energy is used in dental laser treatment to accurately cut through tissue, making it a useful instrument for lesion excision and biopsies. The laser removes a small, targeted portion of tissue during a biopsy with minimum damage to the surrounding tissues. Lasers precisely and neatly remove the entire abnormal growth to remove the lesion. The ability of the laser to coagulate blood vessels as it cuts leads to less bleeding after using the technique. The laser sanitizes the region, lowering the risk of infection and encouraging quicker recovery. The process is less invasive, and precise and regulated tissue removal is achievable by the laser's precision.
Laser dentistry is useful for biopsy and lesion excision because it is precise, less invasive, and lowers the risk of bleeding and infection. Patients feel less pain and edema compared to traditional surgical treatments, which speeds up their recovery. Successful lesion removal and accurate diagnosis in biopsies depend on the laser's precision in removing the targeted tissue while leaving as much healthy tissue as feasible. Patients find laser operations to be more comfortable due to the decreased requirement for sutures and the faster healing timeframes. The lesion's size and location affect its efficacy but conventional surgical techniques are still required in some circumstances. Laser dental surgery provides a substantial benefit concerning procedure, speed, and patient comfort.
4. Teeth Whitening
Teeth whitening is the method for removing stains and discolouration from teeth while lightening their color. Teeth whitening improves teeth's appearance by dissolving and eliminating intrinsic stains from aging or medication use, and surface stains from foods, drinks, and smoking.
The teeth are treated with a peroxide bleaching gel in laser teeth cleaning and activated by a laser beam. The energy from the laser quickens the bleaching agent's chemical reaction, increasing its potency in eliminating discolourations and brightening teeth. The laser guarantees that the whitening solution seeps deeply and uniformly across all tooth surfaces during the one-session method, conducted in a dental office. The sensitivity and pain some patients feel from traditional whitening techniques are lessened with laser usage.
Laser tooth whitening is effective because the benefits are seen right away. Patients attain a brighter smile faster because of the laser's accelerated whitening process compared to traditional procedures. Consistent outcomes are produced by the laser's accuracy in distributing and activating the bleaching chemical uniformly. Patients report decreased sensitivity since the laser is calibrated to prevent overexposure to the bleaching ingredient after dental laser treatment. The outcomes' durability varies depending on personal habits like nutrition and dental hygiene. Laser teeth whitening works well, but the cost is more costly than other in-office methods or take-home whitening bundles. A Teeth Whitening Procedure provides a rapid, effective, and efficient alternative for clients seeking noticeable whitening effects with no discomfort.
5. Gummy Smile
A gummy smile or excessive gingival display in medicine is a smile that shows too much gum tissue above the upper teeth. A short or hyperactive upper lip, small teeth concerning the gums, excessive gum tissue growth, or an incorrect bite causes the problem.
Gingivectomy or gum contouring, is a laser dentistry technique performed to fix a gummy grin. The extra gum tissue is carefully removed and reshaped with a dental laser during the operation to expose more of the tooth structure. Tissue is carefully removed with the help of the laser's accuracy, shaping the gum line to produce a more harmonious and attractive appearance. The laser closes the tissue while it works, minimizing bleeding and lowering the chance of infection aside from cutting. It yields a shorter recovery period and less discomfort comparing the technique to conventional surgical methods.
Gummy smiles are effectively treated using a dental laser treatment. The surrounding tissues are kept healthy and intact since the laser's precision guarantees that just the extra gum tissue is removed. Patients have less discomfort and recover more quickly because the laser cauterizes tissue and lessens bleeding during the surgery. A more proportionate gum-to-tooth ratio is produced, with instant effects in just one session. The laser's use minimizes the chance of surgical complications and the requirement for sutures. Many cases benefit from laser treatment but the underlying reason for the gummy smile determines how beneficial the procedure is. Additional or different therapies are required in some cases involving the structure of the jawbone or lip mobility. Laser dental surgery provides a quick, easy, and successful option when fixing a gummy grin.
6. Removing Benign Tumors
Benign tumours are non-carcinogenic benign lesions in the tongue, lips, cheeks, gums, or other mouth areas. The tumours are uncomfortable, interfere with normal oral functions, and are removed for both cosmetic and medical reasons, despite not being noncancerous and not spread to other body regions.
A concentrated light beam is used in laser dentistry to eliminate benign malignancies from the mouth. The laser slices through the tissue to remove the tumour with the least amount of harm to the surrounding healthy tissues. Dental laser treatment has several advantages over standard surgical procedures, including less bleeding. Laser lowers the risk of infection by sterilizing the region as it cuts. The process is less intrusive and is done in a dentist's office with little anesthetic, enabling the patient to recuperate more quickly and comfortably.
Benign tumours in the mouth are effectively removed with laser dentistry. Better functional and visual outcomes result from the laser's precision ensuring that the targeted tumour tissue is destroyed, protecting the surrounding healthy tissues. Compared to traditional surgical techniques, patients have less discomfort, edema, and bleeding following surgery. Faster healing times and a lower risk of infection are achieved by the laser's capacity to dilate blood vessels and disinfect the surrounding area. The less intrusive nature of laser surgery lessens scarring and the requirement for sutures. Many benign tumours are removed with laser dental surgery, the efficacy varies based on the tumour's size, location, and nature. More surgical procedures are required when the growths are more intricate or larger. Benign tumours in the oral cavity are removed safely and efficiently with laser dentistry, improving patient comfort and treatment results.
7. Nerve Regeneration
Nerve regeneration is mending or regrowing damaged nerve tissues to return them to normal function. Nerve regeneration is essential to dental health for patients with nerve injury caused by trauma, surgery, or long-term illnesses affecting the nerves in the oral and maxillofacial regions.
Laser dentistry is used with low-level laser therapy (LLLT) or photobiomodulation to promote nerve regeneration. The method stimulates cellular activity by penetrating tissues with particular light wavelengths. The laser light increases blood flow, boosts cellular metabolism, and facilitates the creation of new nerve cells and the repair of damaged ones applied to locations where nerve damage has occurred. Laser dental surgery is a non-invasive process taking multiple sessions with the afflicted area. The energy from the laser lessens pain and inflammation and improves the conditions for nerve recovery.
Numerous research indicates favorable outcomes in the field of nerve regeneration with laser dentistry. Low-level laser therapy is beneficial in boosting nerve regeneration because it improves cellular repair processes and reduces inflammation. Patients with nerve injury treated with laser therapy report less discomfort and better nerve function. The particular laser utilised, its parameters, and the biological reaction of each patient affect how much regeneration occurs and the amount and length of the nerve damage. Laser therapy is a useful tool for treating nerve damage used in conjunction with other therapeutic techniques as part of an all-encompassing treatment strategy. Dental laser treatment provides a non-invasive, pain-alleviating, and successful method of promoting nerve regeneration. More studies and clinical trials, however, are needed to maximise its application and completely comprehend its potential advantages and disadvantages.
8. Treating Cold Sores
Treating cold sores is among the functions of laser treatment. Cold sores or fever blisters are tiny, excruciating blisters that form on or around the lips and are brought on by the herpes simplex virus (HSV-1). Cold sores are infectious sores that sprout due to stress, illness, or sun exposure. Cold sores move through different phases that start with a tingling and itching sensation, develop blisters, and then, create crusts once healed.
Low-level laser treatment, or LLLT, is a technique used in laser dentistry to cure cold sores by directing a particular wavelength of light toward the affected area. Laser therapy speeds up the healing process and lessens the pain and agony of cold sores. The laser light's penetration of the skin and viral lesions lessens viral activity and inflammation. Dental laser treatment encourages tissue regeneration and the local immunological response. The procedure is carried out within the cold sore's growth, and is quick and non-invasive, requiring a few minutes. Even the blister from fully forming is avoided using laser treatment to treat the sore during the tingling phase.
Cold sores are effectively treated using laser dental surgery. Patients get pain alleviation instantly after receiving laser treatment, and the healing process takes much less time than with traditional methods. Laser therapy reduces the frequency and intensity of subsequent outbreaks by lowering the viral load in the treated area. The side effects of laser treatment are negligible because it is non-invasive and repeated as necessary to cure recurrent sores. Laser therapy is not a cure for the herpes simplex virus, but an effective way for people who get cold sores to manage their symptoms and enhance their quality of life. Clinical research and patient testimonials attest to the efficacy of laser therapy, adding a unique attribute to various cold sore treatments.
Which Type of Dental Specialist uses Laser Dentistry?
The type of dental specialist uses laser dentistry.
- Periodontists: Periodontists are dental professionals who specialize in implant placement and the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of periodontal disease. They cure gum disease, replace lost bone and tissue, and perform minimally invasive gum surgeries using laser dentistry. Patients receiving periodontal treatments benefit from shorter recovery times, less pain, and less bleeding because of the accuracy of lasers. The type of dental specialists that use laser dentistry refers to a group of dentists who use laser technology to maximise procedural efficiency, improve patient comfort, and improve treatment outcomes.
- Endodontists: Endodontists are specialists in root canal therapy and the care of the dental pulp. They employ laser dentistry to more thoroughly disinfect root canals, eliminating bacteria and encouraging recovery in a less invasive way, compared to conventional techniques. Endodontic procedures are carried out more precisely and with less discomfort following the procedure due to laser technology.
- Orthodontists: Orthodontists are a Type of Dental Specialist focused on identifying, treating, and preventing abnormalities of the teeth and face, mostly using braces, aligners, and other tools for correction. They use laser dentistry to carry out procedures like gingival sculpting to expose unerupted teeth and enhance the aesthetics of the gum line. Lasers aid in the quicker removal of adhesives, which lessens discomfort and chair time after braces are removed.
- General Dentists: General dentists offer dental services, such as examinations, treatments for oral health problems, and preventive care. Laser dentistry is used to prepare cavities, whiten teeth, perform soft tissue surgeries, and treat cold sores. General dentists address several dental care needs with improved ease and effectiveness because of the adaptability of laser technology.
1. Periodontists
Periodontists are dentistry specialists with a focus on periodontal issues prevention, diagnosis, and treatment and the implantation and upkeep of dental implants. Periodontists pursue extra years of schooling to get comprehensive expertise in such fields following graduation from dental school.
Periodontists employ laser dentistry to address periodontal (gum) problem and associated procedures. They use lasers to accomplish less invasive procedures like pocket reduction, which involves taking bacteria and inflammatory tissue out of the periodontal pockets. It encourages the repair and renewal of healthy gum tissue. Scaling and root planing are procedures that employ lasers to thoroughly clean teeth's root surfaces and remove tartar and plaque. Lasers are used in gum grafting, bone regeneration, and crown lengthening treatments to improve accuracy and shorten recovery times. The use of laser technology in such treatments results in reduced bleeding, less discomfort, and quicker recovery when compared to conventional methods. Specialists called Periodontists employ lasers in periodontics due to their accuracy and sterilizing power, which enhances patient comfort and results.
2. Endodontists
Endodontists are dental professionals who specialize in diagnosing, preventing, and treating conditions affecting the surrounding tissues and the dental pulp, the deepest part of the tooth that contains blood vessels and nerves. Endodontists' most well-known practices involve root canal therapy and other treatments meant to preserve teeth.
Endodontists employ laser dentistry for endodontic procedures and root canal therapy. Lasers are used during root canal procedures to precisely remove germs, debris, and infected tissue from the root canals, effectively disinfecting and cleaning them. It improves the cleaning procedure's efficiency and fosters better healing results. Lasers are utilised in endodontic procedures like apicoectomies, where they remove diseased tissue at the root tip and close the canal. The danger of infection is decreased, bleeding is reduced, and recuperation durations are accelerated by using lasers during the surgeries. Lasers treat periapical abscesses by sterilizing the afflicted area and emptying the abscess. Specialists called Endodontists benefit greatly from the precision and efficiency of laser technology, which raises the comfort and success rate of endodontic procedures.
3. Orthodontists
Orthodontists are dental professionals who identify, treat, and prevent abnormalities of the teeth and face. Orthodontists' primary focus is on employing braces, clear aligners, and other orthodontic products to realign mismatched teeth and jaws and improve oral function and visual appeal.
Orthodontists employ laser dentistry in various treatments to improve treatment effectiveness and patient comfort. Lasers are employed in gingival contouring, which reshapes the gum line, particularly around teeth with excessively covered or short gums. It produces more uniform gum shapes and enhances the smile's attractiveness. Brackets and other orthodontic appliances are easily placed when unerupted or partially erupted teeth are exposed due to the application of lasers. The accurate, non-invasive method decreases bleeding and expedites healing. Lasers eliminate the adhesive residue on teeth after braces are taken off, giving the patient a speedier and more comfortable procedure. Specialists called Orthodontists conduct such treatments with more precision, less discomfort, and faster healing times than conventional methods because of laser technology usage.
4. General Dentists
General dentists are primary dental care providers who provide different services to preserve and enhance oral health. General dentists provide initial protection and solutions against oral health difficulties, handling preventive care, diagnoses, and treatments for various dental ailments.
General dentists employ laser dentistry to improve patient comfort and treatment results in various dental care areas. Cavity preparation with lasers preserves more healthy tooth structure while precisely removing decaying tissue than traditional drills. The method lessens the discomfort experienced by patients and lowers the demand for anaesthesia. Lasers offer a noninvasive option for soft tissue surgeries, including frenectomies and gum disease treatment, leading to less bleeding, a lower risk of infection, and quicker recovery times. General dentists employ lasers for cosmetic operations like tooth whitening to get faster and more efficient outcomes. The laser activates the bleaching ingredient. Lasers treat canker and cold sores since they lessen discomfort and hasten healing. General dentists provide different less intrusive, more comfortable, and faster treatments than traditional approaches because of the versatility and precision of laser technology.
What are the Advantages of Laser Dentistry?
The advantages of laser dentistry are listed below.
- Less intrusive method: Dental procedures are carried out more precisely than with conventional techniques because of the use of highly concentrated light beams. Laser dentistry lessens the demand for disruptive tools such as scalpels and drills, which minimize tissue damage. Patients feel less pain and suffering during and following the surgery.
- Prevents teeth trauma: The mechanical stress that conventional dental instruments place on teeth is reduced when lasers are used. The accuracy lowers the chance of fractures and weakening by preserving more of the good tooth structure. Laser dentistry is helpful for sensitive treatments like cavity removal where using too much force damages the surrounding enamel.
- Faster recovery and a shorter healing period: Recovery times from laser treatments are faster than conventional methods. Less damage is sustained overall, and healing occurs more rapidly because the laser targets tissue accurately. Patients resume their regular activities sooner as they feel less swelling and discomfort.
- Suitability to patients with sensitive teeth: Laser dentistry provides a less painful alternative to standard procedures for patients with sensitive teeth. The laser' ability to minimize discomfort, lowers anaesthesia requirement. It results in less anxiety and more comfort during dental visits for patients with increased sensitivity.
- Less infection and bleeding: Laser dentistry provides a less uncomfortable substitute to standard methods for clients with sensitive teeth. The laser' ability to minimize discomfort, lessens the requirement for anaesthesia. It results in less anxiety and greater ease and reduced worry during dental appointments for patients with increased sensitivity.
What are the Disadvantages of Laser Dentistry?
The disadvantages of laser dentistry are listed below.
- High Cost: Laser dentistry entails higher expenditures than standard dental procedures. Patients must pay more for laser treatments because the sophisticated machinery and technology needed are costly. Laser procedures are not covered by most dental insurance plans, resulting in higher out-of-pocket costs.
- Incapacity to remove damaged oral restorations: Amalgam fillings and crowns are examples of old or damaged restorations that lasers fail to remove. Traditional dental instruments are required for such procedures restricting the use of laser dentistry in specific circumstances.
- Incapacity to treat interdental cavities: Interdental cavities are spaces between teeth that are difficult for lasers to reach and cure efficiently. Traditional procedures remain the favored choice because of the laser beam's precision and concentration on more accessible surfaces for interdental cavities. The constraint leads to a less adaptable cavity treatment strategy.
- Incapacity to treat severe tooth decay: Deeply ingrained severe tooth decay needs substantial treatment and restoration, which lasers do not deliver. Decaying tissue is completely removed more successfully using conventional drilling techniques, making laser dentistry not a beneficial option for patients who have extensive decay.
- Incapacity to treat teeth with fillings: Laser treatment is not recommended for teeth that currently have metal fillings. The laser has an adverse influence on the filling materials, increasing risks and decreasing procedure effectiveness. Patients who already have restorations need to receive additional care using traditional dental methods.
What are the Things to Consider for Laser Dentistry?
The things to consider for laser dentistry are listed below.
- Safety: Laser dentists ensure that the equipment is operated safely to reduce harm to patients and dental personnel. Adherence to safety protocols and appropriate training are crucial in preventing unintentional tissue damage or eye problems resulting from laser exposure. Laser equipment must satisfy regulatory requirements and is routinely serviced for safe practice.
- Price: Dental offices and patients find the cost of laser dentistry a major consideration. Laser technology brings many benefits such as shorter recovery times and less discomfort, but the initial outlay and continuing maintenance costs are high. Practices must assess the advantages of the technology against its drawbacks to establish if laser technology is feasible given its financial limits.
- Efficiency of procedure: Laser dentistry offers more effective therapy than traditional approaches with operations taking less time and having fewer consequences. Lasers provide tailored therapy minimizing the need for additional interventions and shortening patient chair times. The intricacy of the case and the practitioner's level of experience affect how effective laser operations are.
- Healing Period: The advantage of faster healing times than with traditional methods is one benefit of laser dentistry. Lasers expedite patients' recuperation by accelerating tissue regeneration and easing postoperative pain. The precise healing time changes based on the procedure employed and the patient's general health and unique healing reaction.
- Sensation during the process: Patients' experiences differ from traditional approaches. Patients are expected to feel some warmth or pressure during treatment, despite its ability to lessen discomfort and the need for anesthetic in certain situations. Dentists must talk with their patients to manage expectations and address any concerns regarding sensations during laser operations.
- Flexibility of usage: Laser technology is used for various dental operations due to its versatility, including cavity preparation, teeth whitening, and soft tissue surgeries. Dentists modify the laser's settings to accommodate varying patient preferences and treatment requirements. Practitioners must possess extensive training and expertise to properly apply laser technology to various operations and patient demographics.
What is the Average Cost of Laser Dentistry?
The average cost of laser dentistry varies greatly based on the particular technique, the dentist’s expertise, and the area of procedure. Laser dentistry in the UK falls between £50 and £2,000. For instance, the average cost of an ulcer treatment is £75 per lesion. Gingival hyperplasia starts at £125 per site, whereas gum contouring or laser periodontal therapy starts at £395 per quadrant. The cost of gingival depigmentation is £1,125 per arch, while the cost of a per-site opportunistic bacterectomy is £125. Tooth crown lengthening surgery costs £100 per tooth
, Periodontal flap surgery costs £400 for one jaw, while periodontal treatment costs £80 per tooth. Dental laser treatment prices are charged from £100 to 150 per treatment. The cost of laser teeth whitening at the Myra Dental Clinic in Turkey is £350 a visit, while the cost for tooth whitening at the same facility is £385. Myra Dental Clinic offers a home teeth whitening kit at £140.
Patients find value in laser dentistry despite the increased expenses because of its advantages, which include less discomfort, less bleeding, quicker recovery times, and a decreased risk of infection. Dental insurance policies differ in their coverage of laser operations where some do not cover cosmetic procedures like teeth whitening. Other dental insurance packages pay a portion of the cost, particularly for medically required treatments. Laser dentistry is more expensive than traditional techniques, still, many patients seek its effective and minimally intrusive dental care.
What are the Risks of Laser Dentistry?
The risks of laser dentistry include vision impairment, skin burns, harm to other structures, and emitted laser plumes. Vision impairment is a considerable danger of laser dentistry. The powerful laser light causes serious eye damage if the staff and dentists do not wear appropriate protective eyewear. Severe vision loss results from even a brief exposure to the laser beam, highlighting the importance of strict safety procedures.
- Skin burns are experienced when the laser is used carelessly or pointed in the wrong direction. The high-energy beams used in laser dentistry have the potential to thermally damage skin, resulting in excruciating burns that need medical care. Another potential danger is damage to nearby structures, especially if the laser is pointed toward sensitive areas like bones or tissues. Inadvertent damage to such structures is caused by improper laser settings or alignment, which makes the patient's recuperation more difficult.
- Respiratory risks are associated with emitted laser plumes such as smoke and particle matter generated during laser treatments. Dental practices must utilise adequate ventilation and smoke evacuation systems because the plume contains dangerous biological material. Appropriate training and attention to safety procedures are crucial to reduce such dangers. Dental practitioners need to be well-versed in laser operation and maintenance to guarantee safe and efficient procedures. Regular calibrations and inspections of equipment are required to prevent unintentional accidents.
Patients must know the potential risks and advantages of laser dentistry before receiving treatment. Informed consent is essential for patients to make knowledgeable decisions about the treatment of their oral health. Laser dentistry has comparatively low dangers. Select a trained dentist because applying the incorrect wavelength or power level causes tissue injury. Some doctors are concerned that advertisements are encouraging more laser treatment than is truly necessary.
Is Laser Dentistry Painful?
No, laser dentistry is not painful. Laser dentistry is developed to reduce pain during and after dental treatments. laser dentistry provides tailored treatment due to its precise technology which eliminates the need for painful tools like scalpels and drills. Lasers' dental functions such as gum reshaping and efficient removal of decaying tissue provide less stress on the surrounding cells, reducing post-procedural swelling and discomfort.
Laser dentistry requires less anesthetic than conventional dentistry, according to data from clinical research and patient reports. Patients experience warmth or slightly tingly sensation instead of the intense discomfort associated with traditional dental tools. For example, the laser's ability to coagulate blood vessels decreases bleeding and inflammation during soft tissue operations like gum contouring, lessening pain and expediting healing.
The tooth's nerve endings become less sensitive when lasers are used for treatments like cavity removal, making the patient feel more at ease. Lasers are advantageous for people who have low pain thresholds or dental anxiety because they make the procedure more bearable since they are non-invasive and need less local anesthetic. Laser dentistry is often connected with less pain but each patient feels pain differently, making it a preferred alternative for many dental treatments.

Why is it Important to find a Qualified Dental Professional for Laser Dentistry?
Finding a qualified dental professional for laser dentistry is crucial because it ensures the safety, effectiveness, and success of the procedure. Qualified dental professionals finish a thorough training program in the use of laser technology. The program covers the proper settings for various treatments, managing potential hazards, and skillfully integrating laser use into entire treatment programs. The knowledge reduces the dangers of laser dentistry, including heat damage, blurred vision, and damage to nearby tissues.
A skilled practitioner precisely aims the laser to address the particular dental problem without harming the surrounding healthy tissues. For example, a trained dentist accurately removes unhealthy tissue with a laser during periodontal therapy, accelerating recovery and minimizing discomfort. A larger risk of problems, such as needless tissue damage and longer healing times, arises from a lack of precision.
Patients who receive treatment from medical practitioners with specific laser training have better results. Research shows that patients experience less discomfort, a decreased risk of infection, and a speedier recovery time when treatments are managed by skilled dentists than when procedures are handled by less experienced dentists. Skilled practitioners are prone to remain current on the newest developments and industry best practices in laser dentistry, which raises the standard of care even further.
A qualified dental professional accurately assesses whether laser dentistry is the most appropriate treatment option for a patient's specific needs. Not every dental problem is best solved by a laser where an experienced practitioner knows when to use laser technology or a more conventional technique.
Are Special Glasses Needed for Laser Dentistry?
Yes, special glasses are needed for laser dentistry. High-intensity laser beams are used in laser dentistry, which carries significant dangers to the eyes if appropriate precautions are not taken. Particular safety glasses are made especially to shield the eyes from the particular laser light wavelengths used in dental operations. The glasses are necessary for the patient and the dental team to avoid unintentional eye exposure, which results in either temporary or permanent vision damage.
The protective glasses constructed of materials that reflect or absorb it keep the laser light from entering the eyes. Varieties of dental lasers, such as diode, CO2, and Nd operate at many wavelengths to effectively protect, requiring the matching of safety glasses to the laser's particular wavelength. Practitioners lessen the chance of eye harm by ensuring that the laser light's intensity is adequately lowered to safe levels through proper eyewear.
The usage of such protective eyewear is strongly recommended by clinical guidelines and laser safety evidence. Suitable laser safety eyewear is mandated by regulatory agencies and professional organizations including the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) and the American National Standards Institute (ANSI). Following the recommendations improves laser dentistry operations' safety while guaranteeing adherence to safety laws.





